
The Expert Field Medical Badge (EFMB) is a prestigious award recognizing medical excellence in field operations. It evaluates both theoretical knowledge and practical skills under challenging conditions, ensuring readiness for real-world scenarios.
1.1 Overview of the EFMB and Its Significance
The Expert Field Medical Badge (EFMB) is a prestigious recognition of exceptional medical competence in tactical environments. It evaluates both theoretical knowledge and practical skills, ensuring medics can operate effectively in combat and field settings. The badge signifies mastery of critical medical tasks, making it a cornerstone of military medical excellence and a mark of distinction for field medics.
1.2 Purpose of the EFMB Study Guide
The EFMB Study Guide provides a comprehensive overview of the test content, helping candidates identify key areas of focus. It serves as a valuable resource to supplement individual study, ensuring familiarity with the exam format and subject matter. While it does not provide answers, it guides effective preparation by aligning study efforts with the test’s requirements and expectations.
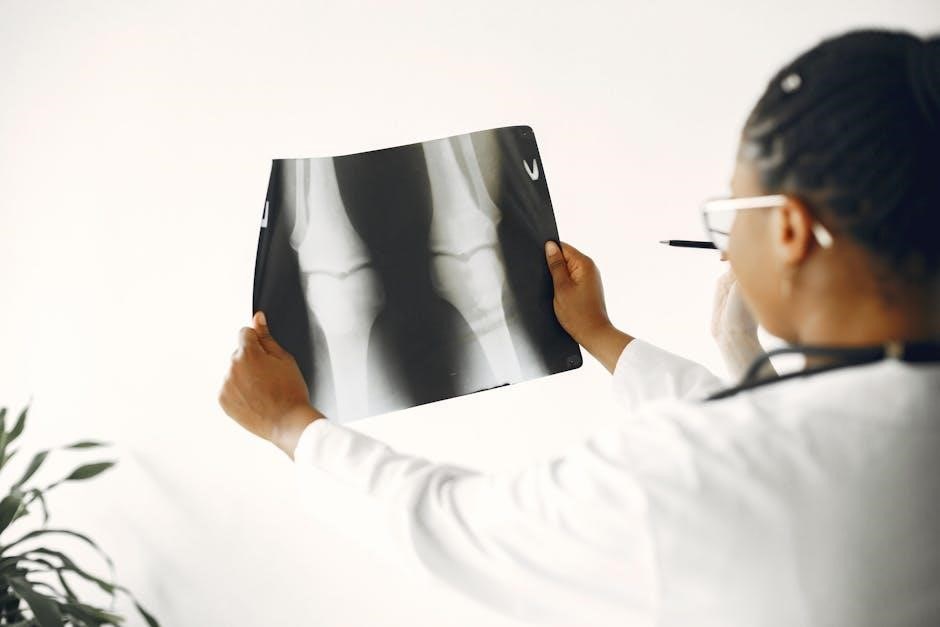
Written Test: Content and Format
The EFMB Written Test is a comprehensive evaluation of theoretical knowledge, covering critical medical skills and trauma care. It is digitally administered, ensuring a standardized assessment of competency.
2.1 Radiology: Imaging Trauma Patients in a Deployed Setting
Imaging trauma patients in deployed settings requires portable, efficient tools. Radiographs and CT scans are critical for assessing injuries. Ultrasound, like FAST exams, aids in detecting internal bleeding. Radiation safety measures, including thyroid shields and distance, are emphasized to protect personnel. These imaging modalities are essential for accurate diagnoses and timely treatment in austere environments, ensuring optimal patient care under challenging conditions.
2.2 FAST Exam: Focused Assessment with Sonography for Trauma
The FAST exam is a portable ultrasound used to detect free intraperitoneal fluid, indicating internal bleeding. Performed with a 3-7 MHz curved array probe, it evaluates hepatorenal, splenorenal, pelvic, and pericardial spaces. Sensitivity is 56%, but specificity is higher, making it a valuable tool for rapid trauma assessment in deployed settings, especially when CT scans are unavailable. It aids in timely decision-making for critical care.
2.3 Computed Tomography (CT) Scanning in Trauma Care
CT scanning provides detailed imaging of internal injuries, crucial for trauma care. Typically available at Role 3 facilities, it aids in diagnosing complex injuries like spinal fractures or internal bleeding. An 18g IV is often required for contrast. While CT scans are not portable, they offer superior diagnostic accuracy, guiding precise treatment plans for critically injured patients in deployed settings.
2.4 Radiation Safety and Protective Measures
Radiation safety is critical in trauma care. Lead aprons and thyroid shields are essential for protecting personnel. Maintaining a minimal distance of three feet from the x-ray source reduces exposure. These measures ensure safety while performing imaging procedures, balancing protection with effective patient care in deployed medical settings.

Practical Assessment: Skills and Tasks
The practical assessment evaluates critical medical skills, such as patient assessment, hemorrhage control, and evacuation. These tasks simulate real-world scenarios, ensuring candidates can apply knowledge effectively in high-stress environments.
3.1 Patient Assessment and Triage in the Field
Patient assessment and triage are critical skills evaluated during the practical test. Candidates must demonstrate a systematic approach to evaluating trauma patients, prioritizing care based on injury severity, and applying the MARCH algorithm. Effective triage ensures optimal resource allocation, maximizing patient outcomes in high-stress environments. This skill is essential for field medical operations.
3.2 hemorrhage Control and Wound Management
3.2 Hemorrhage Control and Wound Management
Hemorrhage control and wound management are critical skills assessed in the practical test. Candidates must demonstrate proficiency in applying tourniquets, using hemostatic agents, and managing wounds. Proper techniques ensure minimal blood loss and prevent infection. These skills are vital for stabilizing patients in austere environments, adhering to Tactical Combat Casualty Care (TCCC) principles.

3.3 Evacuation and Transportation of Patients
Evacuation and transportation of patients is a critical practical skill. Candidates must demonstrate ability to safely move patients using litters or stretchers, ensuring spinal stability and minimizing further injury. Knowledge of MEDEVAC and CASEVAC procedures, as well as proper use of evacuation equipment, is essential. This skill directly impacts patient survival and outcomes in combat zones.
History and Evolution of the EFMB
The Expert Field Medical Badge was established in 1964 to recognize exceptional medical skills in the field. It has evolved to reflect modern combat medicine advancements, ensuring relevance and excellence in military healthcare.
4.1 Establishment of the EFMB Program
The Expert Field Medical Badge (EFMB) program was established in 1964 to recognize medical personnel’s exceptional skills in field environments. MG Duncan recommended its creation to honor outstanding performance. The badge signifies expertise in critical medical tasks and is awarded to those who demonstrate mastery of both theoretical and practical skills, reflecting the Army’s commitment to excellence in healthcare.
4.2 Historical Context and Development
The Expert Field Medical Badge (EFMB) originated from the need for standardized medical skills in field environments. Established in 1964, it evolved to reflect advancements in military medicine and changing operational demands. The badge has been refined over decades, incorporating modern medical technologies and tactics, ensuring it remains a relevant marker of excellence in military healthcare.

Study Guide and Resources
The EFMB study guide offers comprehensive resources, including CPGs, flashcards, and online tools, to aid in thorough preparation for both written and practical exams effectively.
5.1 Utilizing CPGs for Effective Preparation
Utilizing Clinical Practice Guidelines (CPGs) is essential for EFMB preparation. These evidence-based resources provide detailed protocols for trauma care, ensuring candidates master critical skills and knowledge. CPGs cover imaging techniques, FAST exams, and radiation safety, aligning with exam topics. They serve as a foundation for both written and practical assessments, enhancing readiness for real-world applications.

5.2 Recommended Study Materials and Flashcards
Official EFMB study guides and flashcards are indispensable for comprehensive preparation. Platforms like Quizlet offer flashcards covering radiology, trauma assessments, and medical protocols. Utilize the EIB Pro app for patrol tasks and the EFMB Written Test Study Guide for structured learning. These resources help candidates master critical skills and knowledge, ensuring confidence and readiness for the exam.

Preparation and Training Strategies
Effective preparation involves structured study guides, practical task practice, and utilizing online resources like Quizlet for flashcards. These strategies build confidence and readiness for the EFMB exam.
6;1 Time Management and Study Plans
Creating a detailed study plan is crucial for EFMB success. Allocate time for each topic, focusing on radiology, trauma assessment, and practical skills. Utilize a 7-week training plan, balancing written and practical preparation. Incorporate regular review sessions and practice tests to ensure mastery of all sections. Consistency and organization are key to achieving readiness.
6.2 Physical Fitness and Mental Readiness
Physical fitness and mental readiness are critical for EFMB success. A structured training plan, including ruck marches and strength exercises, builds stamina. Mental resilience is cultivated through stress management techniques and focus exercises; Candidates must maintain peak physical condition and mental sharpness to excel in both written and practical assessments, ensuring they can perform under pressure in high-stress environments.

Day of the Test: Tips and Essentials
Ensure all required equipment like Alice Pack, wet weather gear, pencils, pens, and notebooks are packed. Bring an 18g IV for CT scans and maintain a 6-foot distance from x-ray units for safety. Essential items include weapon cleaning kits and proper identification.
7.1 Packing List and Required Equipment
Essential items include an Alice Pack, wet weather gear, notebooks, pens, pencils, and an 18g IV for CT scans. Bring a lock for duffel bags, weapon cleaning kits, and M-16A2 rifles with blanks. Proper identification and safety gear like aprons and thyroid shields are also necessary. Ensure all equipment is neatly organized and easily accessible.
7.2 Test Site Requirements and Logistics
The EFMB test site requires adherence to strict protocols, including ID verification and security checks. Candidates must arrive early and be in proper attire. Designated locations like Fort Sam Houston host the event. Ensure all equipment is pre-inspected, and note that electronic devices may be restricted. Logistics vary by site, so verify specifics beforehand to avoid issues.

The Significance of Earning the EFMB
Earning the EFMB signifies exceptional medical competence and dedication. It is a prestigious recognition of a soldier’s ability to deliver superior care in challenging environments, upholding military medical excellence.
8.1 Career Advancement and Professional Recognition
Earning the EFMB enhances career advancement by demonstrating exceptional medical expertise. It distinguishes soldiers as leaders in their field, often leading to promotions and increased credibility. The Expert Field Medical Badge is a prestigious recognition that highlights a soldier’s commitment to excellence, making them highly valued in military medical operations and leadership roles.
8.2 Contribution to Military Medical Excellence
Earning the EFMB signifies a soldier’s commitment to maintaining the highest standards of medical care in field settings. It ensures proficiency in critical skills, enhancing overall military medical capabilities. By fostering expertise, the EFMB contributes to mission success and the preservation of life, embodying the Army’s dedication to excellence in healthcare under challenging conditions.
Common Challenges and Solutions
Candidates often face challenges like time management, stress, and mastering both written and practical components. Solutions include targeted study strategies, practice under pressure, and physical conditioning.
9.1 Overcoming Difficulties in Written and Practical Tests
Candidates often struggle with the written test’s complexity and the practical test’s hands-on demands. To overcome these, focused study guides, realistic practice scenarios, and mental preparation are essential. Utilizing CPGs for written prep and repetitive drills for practical tasks enhance confidence and proficiency, ensuring readiness for both test components.
9.2 Strategies for Success in High-Stress Environments
Succeeding in high-stress environments requires mental resilience and focused preparation. Techniques like deep breathing, positive visualization, and structured time management help maintain calm. Regular physical fitness and mental readiness training build confidence. Staying organized and adhering to established protocols ensure clarity during challenging situations, enabling candidates to perform effectively under pressure.
Earning the EFMB is a testament to dedication and skill. This guide provides a roadmap for success, emphasizing thorough preparation and mental readiness. Stay focused, persistent, and strive for excellence in military medical care.
10.1 Summary of Key Points
The EFMB is a prestigious award recognizing medical expertise in field settings, requiring mastery of both written and practical skills. This guide outlines essential topics, from radiology to patient evacuation, and provides strategies for effective preparation. Utilizing CPGs, study materials, and physical training ensures readiness. Earning the EFMB signifies professional excellence and contributes to military medical superiority.
10.2 Encouragement for Future Candidates
Earning the EFMB is a testament to dedication and skill. Embrace the challenge, stay disciplined, and leverage resources like study guides and mentorship. Perseverance and hard work will lead to success, enhancing your career and contributing to military medical excellence. Your effort reflects commitment to saving lives and upholding the highest standards of care.